The Battle Of Tracheids Vs Vessel Elements: Unveiling Nature’s Architectural Wonders
Tracheids vs Vessel Elements: A Comparative Analysis
Welcome, Element Enthusiast! In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of tracheids vs vessel elements, two crucial components of plant vascular systems. By understanding the characteristics, functions, and advantages of each, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate mechanisms that allow plants to transport water and nutrients efficiently. So, let’s explore these elements and unlock the secrets of their unique properties.
Introduction
Tracheids and vessel elements are both types of cells found in the xylem, the tissue responsible for water transport in plants. These cells play a crucial role in maintaining plant health and survival. While both tracheids and vessel elements serve a similar purpose, they differ in structure and functionality.
1 Picture Gallery: The Battle Of Tracheids Vs Vessel Elements: Unveiling Nature’s Architectural Wonders
Tracheids are elongated cells with tapering ends. They are tube-like structures that allow water to flow through pits, tiny openings in the cell walls. Tracheids are present in various plant species, including ferns, gymnosperms, and angiosperms.
Vessel elements, on the other hand, are wider and shorter cells that form vessels. These vessels are interconnected, creating a continuous pathway for water transport. Vessel elements are primarily found in angiosperms, allowing for efficient water conduction and higher growth rates.
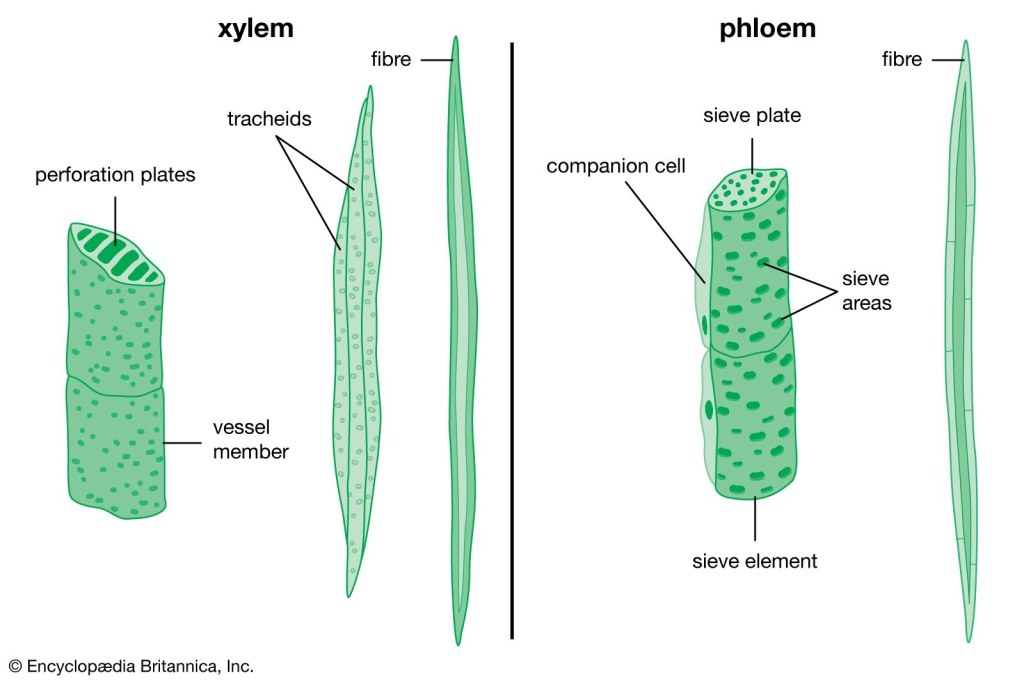
Image Source: britannica.com
Now that we have a basic understanding of tracheids and vessel elements, let’s take a closer look at their main characteristics and functions.
Characteristics of Tracheids and Vessel Elements
Tracheids
1. Structure: Tracheids are elongated cells with tapering ends, resembling microscopic tubes. They have secondary cell walls with pits that allow for water movement.
2. Size: Tracheids are relatively narrow and longer compared to vessel elements.
3. Function: Tracheids play a crucial role in water transport and provide structural support to plants.
4. Distribution: Tracheids are present in a wide range of plant species, including ferns, gymnosperms, and angiosperms.
5. Adaptability: Tracheids are well-adapted to withstand environmental variations and can function efficiently even under harsh conditions.
6. Lignification: Tracheids undergo lignification, a process where lignin is deposited in their cell walls, enhancing their strength and durability.
7. Pits: Pits in the cell walls of tracheids enable lateral water movement between adjacent cells, providing an additional route for water transport.
Vessel Elements
1. Structure: Vessel elements are wider and shorter compared to tracheids. They form vessels by connecting end to end, creating a continuous pathway for water conduction.
2. Size: Vessel elements are wider and shorter compared to tracheids, allowing for efficient water transport.
3. Function: Vessel elements specialize in transporting water and nutrients, contributing to the rapid growth and development of angiosperms.
4. Distribution: Vessel elements are primarily found in angiosperms, enabling higher growth rates compared to plants without vessel elements.
5. Perforations: Vessel elements have perforated end walls called perforation plates, providing an uninterrupted conduit for water and dissolved substances.
6. Secondary Cell Wall: Vessel elements have a less heavily lignified secondary cell wall, which increases their conductivity and facilitates water flow.
7. Efficiency: The interconnected structure of vessel elements allows for greater water conduction, making angiosperms more efficient in nutrient uptake and translocation.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Tracheids and Vessel Elements
Advantages of Tracheids
1. Versatility: Tracheids are present in a wide range of plant species, making them a versatile water transport system.
2. Structural Support: Tracheids provide structural support, enhancing the overall stability of plants.
3. Adaptability: Tracheids can withstand harsh environmental conditions and continue to function efficiently.
4. Lignification: The lignified cell walls of tracheids increase their strength and durability, ensuring long-term functionality.
5. Reducing Embolism: Tracheids have the ability to prevent air bubbles, or embolisms, from interrupting water flow.
Disadvantages of Tracheids
1. Slower Flow: Tracheids have narrower lumens, resulting in slower water flow compared to vessel elements.
2. Limited Efficiency: The pit structure of tracheids can cause resistance to water movement, reducing overall efficiency.
3. Less Conduction Capacity: Tracheids have a lower water conduction capacity compared to vessel elements.
4. Vulnerability to Dysfunction: Blockage of pits in tracheids can lead to dysfunction and hinder water transport.
5. Limited Growth Potential: The slower water flow in tracheids may limit the growth potential of plants.
Advantages of Vessel Elements
1. Efficient Water Conduction: The wider lumens of vessel elements allow for faster water flow and efficient nutrient uptake.
2. Rapid Growth: Vessel elements contribute to the rapid growth and development of angiosperms, enabling them to outpace other plant species.
3. Enhanced Transport Capacity: The interconnected structure of vessel elements provides a high transport capacity, facilitating the distribution of water and nutrients.
4. Reduced Resistance: Vessel elements have lower resistance to water flow compared to tracheids, increasing overall efficiency.
5. Adaptation to Diverse Environments: Vessel elements have evolved to adapt to varying environmental conditions, enhancing the survival and proliferation of angiosperms.
Disadvantages of Vessel Elements
1. Vulnerability to Air Embolism: The perforation plates in vessel elements can make them more susceptible to air embolisms, disrupting water transport.
2. Limited Adaptability: Vessel elements are primarily found in angiosperms, limiting their presence in other plant groups.
3. Potential Weakness: The less heavily lignified secondary cell wall of vessel elements may make them more prone to damage or breakage.
4. Dependency on Living Cells: Vessel elements require living companion cells for proper function, adding complexity to their structure.
5. Susceptibility to Pathogens: The interconnected structure of vessel elements can facilitate the spread of pathogens throughout the plant, posing a risk to overall health.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Are tracheids and vessel elements present in all plant species?
Yes, tracheids are found in a wide range of plant species, including ferns, gymnosperms, and angiosperms. Vessel elements, however, are primarily present in angiosperms.
2. What is the main function of tracheids and vessel elements?
Tracheids and vessel elements are responsible for water and nutrient transport within plants, ensuring their growth and survival.
3. How do tracheids and vessel elements differ in structure?
Tracheids are elongated cells with tapering ends and pits in their secondary cell walls, while vessel elements are wider, shorter, and form vessels by connecting end to end.
4. Which type of element allows for faster water conduction?
Vessel elements have wider lumens, enabling faster water flow and more efficient water conduction compared to tracheids.
5. Can tracheids and vessel elements be damaged or dysfunctional?
Both tracheids and vessel elements can experience blockage or dysfunction, hampering water transport and potentially affecting plant health.
Conclusion
In conclusion, tracheids and vessel elements are essential components of plant vascular systems, enabling water and nutrient transport. While tracheids provide versatility and structural support, vessel elements offer rapid growth and enhanced water conduction. Understanding the advantages, disadvantages, and distinct characteristics of each element allows us to appreciate their roles in plant physiology and adaptability to diverse environments. By studying tracheids and vessel elements, we gain insights into the remarkable complexity of plant anatomy and the mechanisms that drive their growth and survival.
Now that you have gained a deeper understanding of tracheids vs vessel elements, we encourage you to explore further and continue unraveling the mysteries of the plant world. Whether you are a botanist, a nature enthusiast, or a student, the study of these elements opens up a world of knowledge and appreciation for the wonders of nature.
Final Remarks
As with any scientific topic, the study of tracheids and vessel elements is an ongoing process, with new discoveries and insights emerging. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the subject matter based on current knowledge and research. It is essential to consult authoritative sources and continue researching to stay up to date with the latest developments in this field. Now, go forth and explore the fascinating world of tracheids and vessel elements!
This post topic: Element
