The Ultimate Guide: Discover Which Group Of Elements Is The Least Reactive Now!
What Group of Elements is the Least Reactive?
Introduction
Welcome, Element Enthusiast, to this informative article discussing the least reactive group of elements. In the vast realm of chemistry, reactivity plays a crucial role in various chemical reactions. Understanding which group of elements is the least reactive allows scientists and researchers to predict their behavior and discover new applications. In this article, we will delve into the characteristics of the least reactive group of elements, their advantages and disadvantages, as well as answer frequently asked questions regarding their reactivity.
2 Picture Gallery: The Ultimate Guide: Discover Which Group Of Elements Is The Least Reactive Now!
Now, let us embark on this fascinating journey into the world of chemical reactivity!
Table of Contents
![what group of elements is the least reactive - Reactivity Series of Metals - Chart [and How to remember] - Teachoo what group of elements is the least reactive - Reactivity Series of Metals - Chart [and How to remember] - Teachoo](https://uafinance.biz/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/reactivity-series-of-metals-chart-and-how-to-remember-teachoo.jpg)
Image Source: cloudfront.net
What
Who
When
Where
Why
How
Advantages and Disadvantages
FAQ
Conclusion
Final Remarks
What Group of Elements is the Least Reactive?
The least reactive group of elements in the periodic table is the noble gases. Also known as Group 18 or Group 0, these elements include helium (He), neon (Ne), argon (Ar), krypton (Kr), xenon (Xe), and radon (Rn).
The noble gases are characterized by their full outer electron shells, making them stable and unreactive. As a result, these elements exhibit low chemical reactivity, rarely forming compounds with other elements.
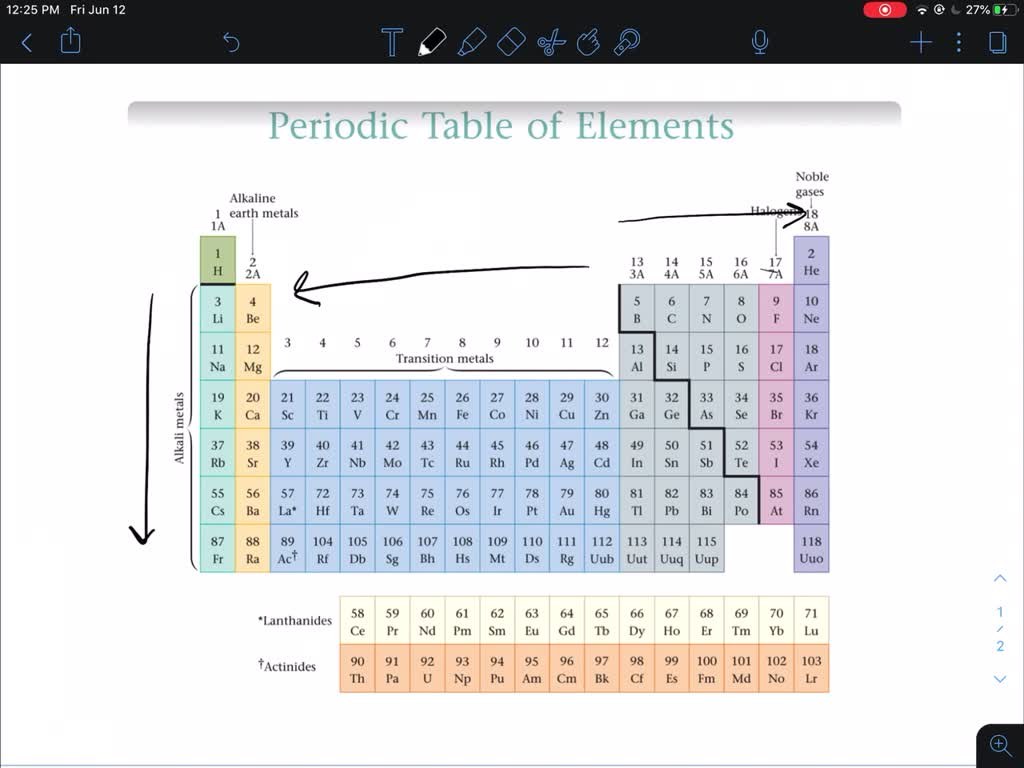
Image Source: numerade.com
🔍 Fun Fact: The term noble gases originated from their relatively inert and noble-like behavior.
Who Discovered the Least Reactive Group of Elements?
The discovery and understanding of the least reactive group of elements can be attributed to various scientists throughout history. In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, notable chemists such as Sir William Ramsay and Lord Rayleigh conducted experiments that led to the discovery of noble gases.
🔍 Fun Fact: Sir William Ramsay and Lord Rayleigh were jointly awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1904 for their investigations on noble gases.
When Were the Least Reactive Group of Elements Discovered?
The discovery of the least reactive group of elements occurred over several decades. Sir William Ramsay first discovered helium in 1895, followed by neon, argon, krypton, and xenon in subsequent years. Radon, the heaviest and least reactive noble gas, was discovered by Friedrich Ernst Dorn in 1900.
These discoveries revolutionized our understanding of chemical reactivity and expanded the periodic table.
Where Can the Least Reactive Group of Elements be Found?
The noble gases can be found in trace amounts in the Earth’s atmosphere. Helium, for instance, is often extracted from natural gas deposits. Additionally, noble gases are present in certain minerals and can be isolated through various extraction processes.
However, due to their low reactivity, noble gases are generally not abundant in nature.
Why are the Noble Gases the Least Reactive?
The noble gases are the least reactive group of elements due to their electron configuration. These elements have completely filled outer electron shells, making them stable and less likely to gain or lose electrons.
Since chemical reactions typically involve the transfer or sharing of electrons, the noble gases lack the necessary electron availability to participate in most reactions. Consequently, they rarely form compounds with other elements.
How Can the Low Reactivity of Noble Gases be Explained?
The low reactivity of noble gases can be explained by their electron configuration and the octet rule. The octet rule states that atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons in order to achieve a stable configuration with eight valence electrons.
The noble gases already possess a stable octet configuration, with the exception of helium, which has a full outer shell with only two electrons. This stability makes it energetically unfavorable for noble gases to form chemical bonds, resulting in their overall low reactivity.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the Least Reactive Group of Elements
The least reactive group of elements, the noble gases, offers various advantages and disadvantages in different applications.
Advantages:
Noble gases are commonly used in lighting, such as neon lights and fluorescent lamps, due to their ability to produce vibrant colors.
Helium, a noble gas, is widely used in cryogenics and as a coolant for superconducting magnets.
Noble gases are utilized in certain medical procedures, such as xenon anesthesia and neonatal jaundice treatment.
Argon, a noble gas, is frequently employed as an inert atmosphere in various industrial processes, including welding and metal production.
Noble gases have applications in analytical chemistry, such as gas chromatography and mass spectrometry.
Disadvantages:
Noble gases are relatively rare and expensive to obtain, which limits their widespread use.
The low reactivity of noble gases can hinder their incorporation into certain chemical reactions or compound formations.
Radon, a radioactive noble gas, poses health risks when concentrated in enclosed spaces, such as basements.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Are noble gases completely inert?
No, noble gases are not completely inert. While they are the least reactive group of elements, there are a few known compounds where noble gases can combine with other elements under certain conditions.
2. Can noble gases form chemical bonds?
Noble gases can form weak chemical bonds with highly electronegative elements, such as fluorine and oxygen. However, these compounds are typically unstable and require specific conditions to exist.
3. Are noble gases harmful to humans?
Noble gases, in their pure form, are generally non-toxic. However, certain noble gas compounds or isotopes, such as radon, can pose health risks if inhaled or ingested in high concentrations.
4. Can noble gases be used as energy sources?
No, noble gases cannot be used as energy sources as they do not undergo combustion or release energy during normal chemical reactions. However, helium has applications in cryogenics and fusion research.
5. Can noble gases be found in outer space?
Yes, noble gases have been detected in outer space. They are part of the interstellar medium and can be observed in the spectra of stars and other celestial objects.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the noble gases, comprising helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, and radon, are the least reactive group of elements due to their stable electron configurations. Their low reactivity makes them valuable in various fields, from lighting and medical applications to industrial processes and analytical chemistry. However, their scarcity and limited reactivity also present certain drawbacks. Understanding the least reactive group of elements provides valuable insights into the fundamental principles of chemical reactivity and enables advancements in various scientific and technological domains.
Final Remarks
As we conclude this exploration of the least reactive group of elements, it is important to acknowledge the significant contributions of scientists throughout history in uncovering the properties and applications of noble gases. The study of chemical reactivity continues to evolve, leading to exciting discoveries and innovations that shape our understanding of the world.
Disclaimer: The information presented in this article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered as professional advice. Always consult with a qualified chemist or scientist for specific inquiries regarding the reactivity of elements.
This post topic: Element

